What is Quality Lifecycle Management (QLM)?
Throughout the product development lifecycle of any product, the factor of quality is significantly important as it has direct impact on an organization’s bottom line. Retaining complete control over product quality through development and maturity lifecycle phases is essential to ensure high quality products, customer loyalty, and increased profitability. This is easier said than done and why quality lifecycle management (QLM) comes into play.
What is QLM?
Quality lifecycle management (QLM) is a systematized approach to managing all facets of product quality, reliability, and risk throughout the product development lifecycle. Methods fully incorporate all phases of the supply chain and involve stakeholders from conception to manufacturing. Manufacturers can unite all quality related activities across the supply chain for a cohesive understanding of supplier quality to fulfill product quality.
Adopting QLM for Supply Chain Visibility
Traditionally, quality management processes in the supply chain operate in silos. The goal of quality lifecycle management (QLM) is to create an integrated supply chain with a holistic view of quality. This includes integrating once independent components of quality into a synergistic, functional supply chain with improved quality control accuracy.
QLM looks at the entire supply chain to address quality on a comprehensive scale, that elevates touchpoints between all stakeholders. This makes for a robust tool in implementing continuous improvements to quality systems and processes to produce high quality products.
Centralize the Supply Chain
Everyone knows what is going on at any given moment. QLM organizes how a supply chain collaborates, communicates, and shares information with centralized workflow. For example, engineering knows exactly what components are necessary to meet functional requirements, purchasing knows what materials need to be sourced, manufacturing understands what operating procedures to perform, quality knows if the current product is up to par with the quality standards, and management knows it has a complete set of data to base its business decisions on.
All in all, QLM creates a united format for product quality, risk, and reliability through the entire product development lifecycle.
Knowledge Sharing & Collaboration
QLM enables a systemized feedback loop that relays pertinent information to parties that need to receive it when they need to receive it. Lessons learned can be recorded from one department, stored as best practices, and later referenced by another to adopt product improvements in other similar situations.
Promoting a collaborative supply chain through knowledge sharing not only improve product quality, but also reduce time wasted in production process planning. Allowing shared information across the supply chain allows feedback to be received in a timelier manner to escalate problems much faster.
Components of Quality Lifecycle Management
Quality lifecycle management is comprised of the following set of processes: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control, and quality improvement. A QMS (quality management system), such as Empower QLM, is software that helps organize information and oversee these processes to ensure product quality is fully met.
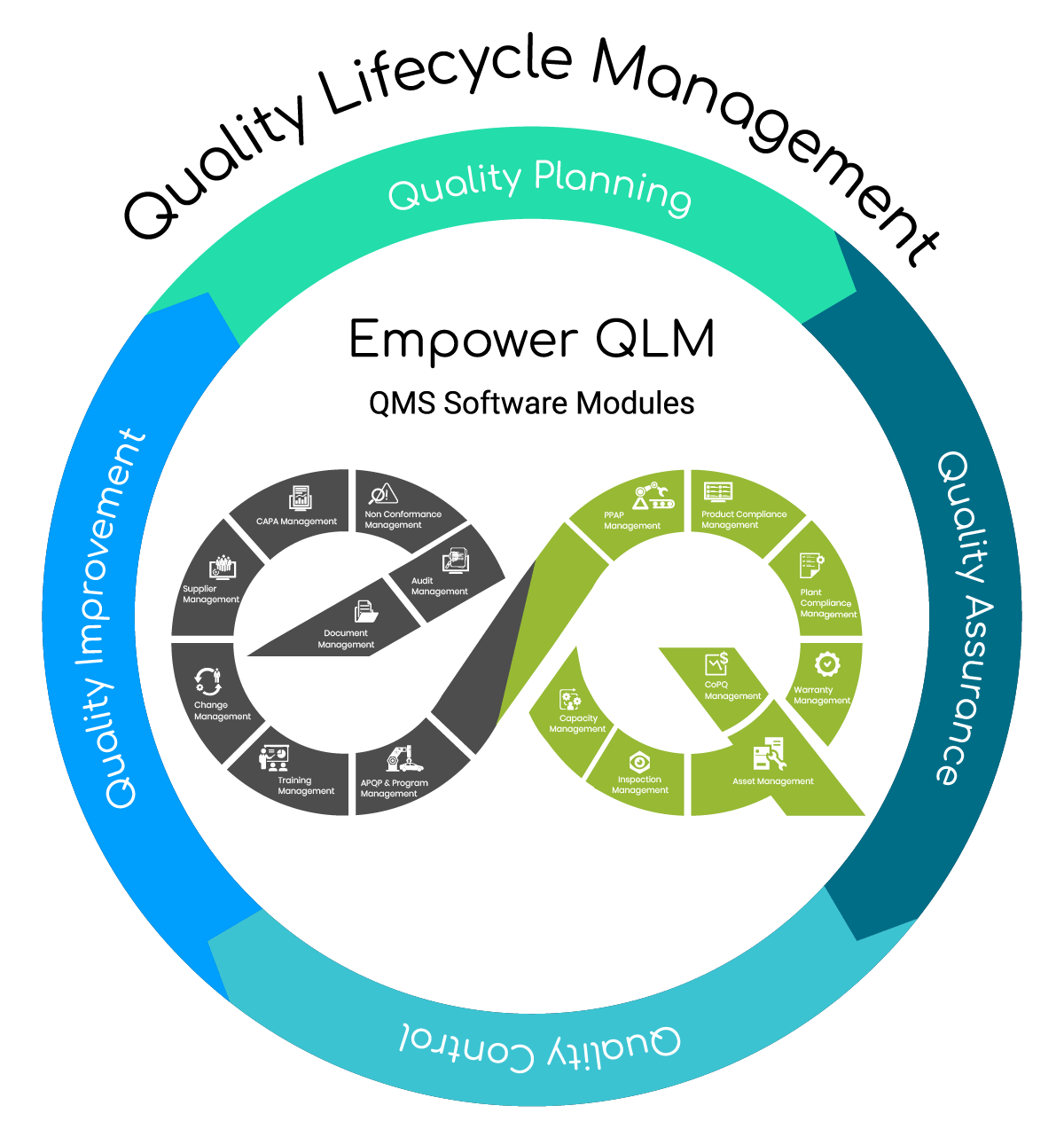
Quality Planning (Review Requirements)
A systemized guide on how to fulfill quality requirements.
The focus of quality planning is taking all the information prior to beginning a project and translating it into a tangible action plan. A quality plan outlines what needs to be done at what standard of quality, and how to measure quality standards and prevent defects. The process includes identifying product requirements to develop processes that will meet those requirements through production to deliver high quality, reliable, and safe finished goods.
- Review and verify product/process requirements to manage quality, reliability, and risk.
- Determine quality objectives and standards.
- Identify conditions to meet quality standards.
- List tools and techniques that quantify quality standards through measurement.
Tools for Quality Planning (Analyze)
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Benchmarking
- Flowcharting
- Design of experience
- Cost of Quality
Quality Assurance (Verify Process)
Application of processes to fulfill quality requirements.
The focus of quality assurance is to enact the systemized activities outlined in a quality plan meet obligated quality standards through production. Quality assurance activities run parallel with production. The goal of preventing problems from happening before they happen by being proactive in strategic application of quality functions.
This provides confidence that production processes are serviceable in meeting quality standards. For example, a quality assurance team uses quality plan as a procedural guide to assess, verify, and monitor production processes for continuous improvements. QLM enables a procedural process to make sure all functions run through the checks before moving on to the next step.
Tools for Quality Assurance (Audit)
- Quality planning tools
- Quality audits
Quality Control (Validate Products)
Make sure products fulfill quality requirements.
The focus of quality control is to validate that the implemented processes worked to meet product quality requirements. This includes inspecting product design for quality defects and corrections. Inspection is a key component of quality control to confirm alignment with standards of quality. In today’s environment, manual inspections are ineffective with the possibility of overlooking a step or simple human error. Therefore, the need for a quality management system with tools to automate quality lifecycle management is critical.
Tools for Quality Control (Inspect)
- Inspection
- Control charts
- Pareto diagram
- Statistical sampling
- Trend analysis
Quality Improvement (Implement Lessons Learned)
Make ongoing changes to improve quality.
The focus of quality improvement is to continuously improve production processes to eliminate CoPQ, reduce waste, and eliminate inefficiencies. Lessons learned takes a methodical approach to transfer experience and knowledge acquired from one project to future project. Application of lessons learned reduces expensive mistakes and mitigate risks associated with producing poor quality products. Sharing lessons learned with supply chain stakeholder’s is instrumental to for everyone to be on the same page.
Quality lifecycle management (QLM) is a critical piece of the product development lifecycle. Implementing the right QMS technology helps ensure products are being produced accurately, consistently, and with high quality. Empower QLM is the pioneer in developing QMS technology that fully supports QLM. Using a zero defects approach, Empower QLM uses built-in checks and control for each stage to certify proper management of products through the supply chain.
About Empower QLM
Empower QLM, a division of RGBSI, is a cloud-based quality management system (QMS) for total quality lifecycle management (QLM). The technology is the only QMS on the market that enables PPAP automation as result of APQP. It establishes compliance with industry-specific standards across the automotive, aerospace, defense, medical, locomotive, and energy & power generation sectors. From product conception through manufacturing, Empower QLM provides complete transparency by connecting all relevant parties, including the supply chain.
Looking for QMS technology to better manage processes and products?
Browse Software and Service Solutions
Need help with your quality lifecycle management activities?
Download Empower QLM Software Overview Brochure
