What is a Control Plan?
A control plan – what is it? What are the different types of control plans? How is a control plan used and developed to implement quality control measures? Here is a high level overview of control plans to address these questions.
What is the definition of a control plan?
A control plan is a living document that outlines the methods taken for quality control of critical inputs/features to deliver outputs/products that meet customer requirements.
Control plans are:
- Maintained in real-time
- Written descriptions of the measurements, inspections, and checks put in place to control production parts and processes.
- Updated if process changes occur or new processes are implemented to submit for a new PPAP if required.
Direct Inputs into a control plan:
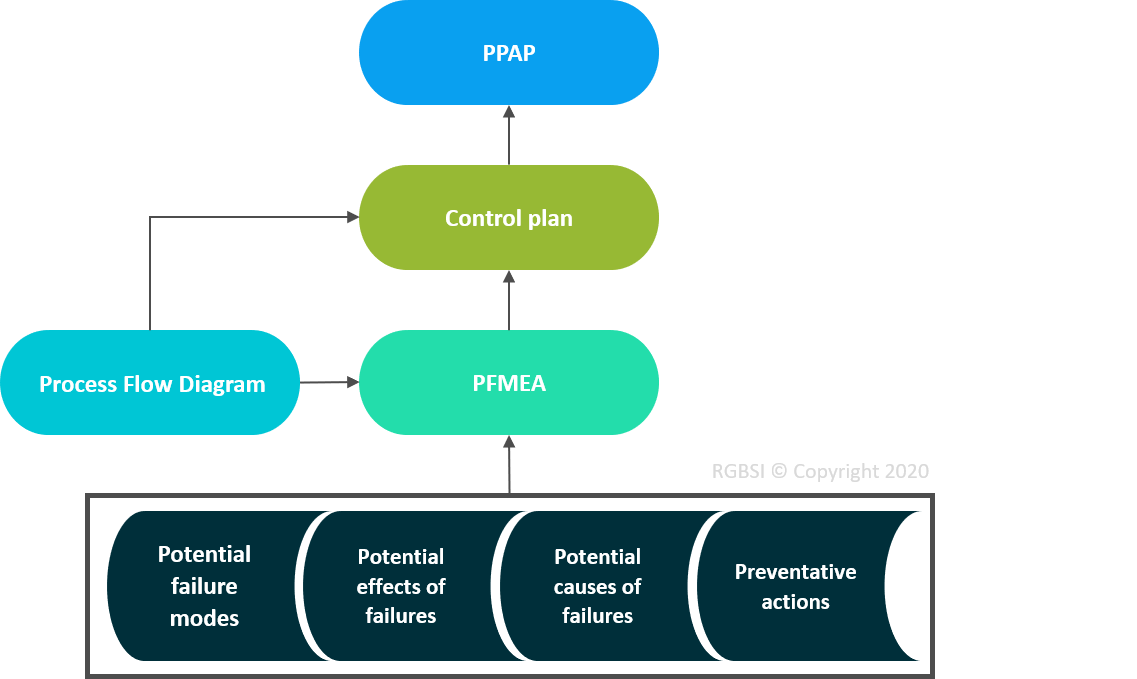
- Process flow diagram
- PFMEA (process failure mode effects analysis)
Information Flow
A control plan is comprised of information gathered from various sources, such as a process flow diagram and PFMEA. This information is used to build a comprehensive plan of action in understanding production processes and identifying potential issues to ensure production quality meets customer requirements.
Process Flow Diagram (“What does the process do?”)
This shows process flow and identifies process inputs and outputs.
PFMEA (“What could go wrong? Is it preventable or detectable?”)
This uses the process flow diagram to detect potential issues in the production process.
Control Plan (“What needs to be controlled or monitored? How do we react to problems?”)
This creates a plan based on the process flow diagram and PFMEA to control quality.
Types of Control Plans
There are three types of control plans that correspond to different phases in the production. The control plan used depends on which processes are being monitored.
Prototype control plan
- Applicable if a component is in the early phase of development.
- Includes: descriptions of dimension measurements, materials, and performance tests during a prototype development.
Pre-launch control plan
- Applicable when the prototype phase is complete for a component, but full production stability is not yet achieved.
- Includes: descriptions of dimension measurements, materials, and performance tests conducted after the prototype phase is complete with increased quality checks and frequency.
Production control plan
- Applicable when a component is in full production.
- Includes: characteristics, process controls, tests, and measurements conducted through full production.
Process to Develop a Control Plan
The Benefits of a Control Plan
Quality Benefits:
- Reduces waste/non-conformance
- Ensures the quality requirements of products are met.
- Provides a thorough evaluation of the product and process with structure and discipline.
Customer Benefits:
- Focus resources on process and product characteristics important to customers
- Better allocation of resources to reduce expenses without sacrificing quality.
The Importance of a Control Plan
Control plans help suppliers overcome critical challenges and focus on product quality, process efficiency, and expense reduction.
About Empower QLM
Empower QLM, a division of RGBSI, is a cloud-based quality management system (QMS) for total quality lifecycle management (QLM). The technology is the only QMS on the market that enables PPAP automation as result of APQP. It establishes compliance with industry-specific standards across the automotive, aerospace, defense, medical, locomotive, and energy & power generation sectors. From product conception through manufacturing, Empower QLM provides complete transparency by connecting all relevant parts of the supply chain.
Looking for QMS technology to better manage and align process flow diagrams, PFMEA, and control plans?